- Home
- Arthroscopic Repair Of SLAP Tear
Arthroscopic Repair Of SLAP Tear
What is a SLAP tear?
SLAP stands for “superior labrum from anterior to posterior.” This type of shoulder labral tear occurs at the top (“superior”) of the glenoid labrum where it connects to the biceps tendon, and it extends in a curve from the chest (“anterior”) to the back (“posterior”). SLAP lesions are considered as separate entities from other labral tears because the superior labrum is the attachment site of the long head biceps tendon. Injuries to the labrum in this region can result in labral symptoms, biceps symptoms or both.
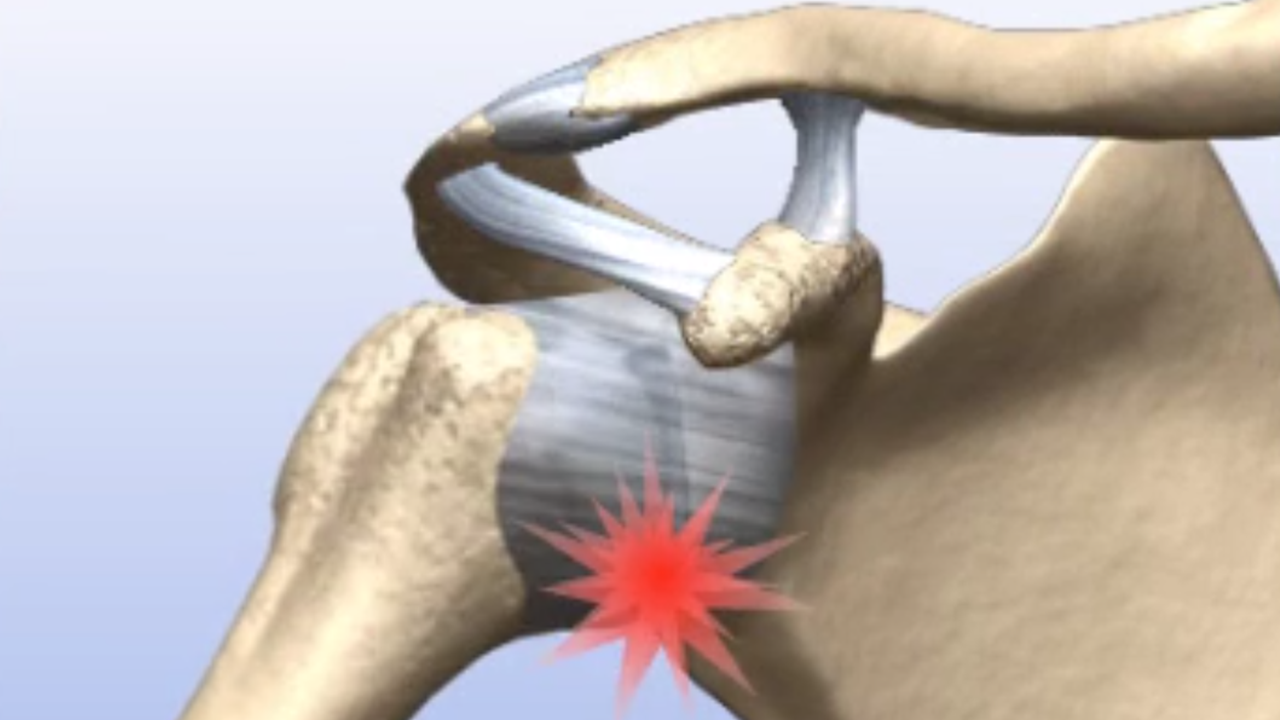
What causes a SLAP tear?
SLAP tears can be caused by falling onto an outstretched hand, quickly lifting a heavy object or from a forceful, overhead arm motion during sports or work activity. More often, however, they result from repetitive stress on the shoulder which, over time, wears down the shoulder labrum.
In both cases, SLAP tears are most common among people whose daily activities require frequent upward arm movement, such as weightlifters, tennis players and factory or shipping workers.
SLAP tears are sometimes a result of or found in combination with biceps tendonitis or a biceps tendon tear. If a biceps tendon is torn away from where it connects to the scapula bone (shoulder blade), it can tear the glenoid labrum along with it.
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT
First Choice for Orthopedics &
Joint Replacements
What are the symptoms of SLAP tear?
SLAP tears can cause pain and range-of-motion problems in the shoulder labrum, the biceps tendon or both. Common symptoms of a SLAP tear include:
- dull or aching pain in the shoulder, especially while lifting over the head
- a painful feeling of clicking, popping or grinding in the shoulder during movement
- difficulty performing normal shoulder movements
- pain at the front of the shoulder near the biceps tendon
- limited range of motion
How is SLAP tear diagnosed?
Diagnosing a SLAP tear is challenging, especially since they often occur in conjunction with other injuries to soft tissues of the shoulder and upper arm. A sports medicine physician will review your medical history, symptoms and the circumstances under which your injury occurred. If your doctor to suspects a SLAP tear, they will order soft-tissue radiological exams. This is usually an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
How is a SLAP tear Treated?
SLAP tears may be treated nonsurgically or surgically, depending on the patient’s individual condition. Conservative, nonsurgical treatments including rest and physical therapy are usually tried first, except in severe cases.
Biceps tenotomy
This surgery releases (detaches) the tendon from the labrum.
Biceps tenodesis
In this procedure, the biceps tendon is detached from the shoulder labrum and then reinserted lower down, directly onto the humerus (upper arm) bone, to retain function.
When surgery is warranted, the choice of the appropriate procedure will depend on a person’s age and the specific type of SLAP tear they have. The three most common surgeries for SLAP tears are:
- SLAP repair
- biceps tenodesis
- biceps tenotomy
SLAP repair
SLAP repair is performed arthroscopically, using minimally invasive techniques. Depending on the severity of the tear, the labrum and ligaments may need to be reattached to the bone using sutures and anchors.Patients who experience biceps tendonitis in conjunction with a SLAP tear may need their biceps surgically disconnected from the labrum to relieve the stress it places on it.
Biceps tenotomy
This surgery releases (detaches) the tendon from the labrum.
Biceps tenodesis
In this procedure, the biceps tendon is detached from the shoulder labrum and then reinserted lower down, directly onto the humerus (upper arm) bone, to retain function.



