- Home
- Multiligament Injuries
Multiligament Injuries
Multi ligament injuries
The concept of multiligament knee injuries comprises a wide range of ligament and intra-articular injury patterns. These complicated injuries necessitate a methodical approach to evaluation and treatment. Management strategies for these multifaceted injuries attempt to balance the restoration of stability with maintenance of function through the mergence of operative and nonoperative means. The operative methods include repair, repair plus augmentation, or reconstruction of injured structures combined with bracing and rehabilitation in the short term. Nonoperative treatment is usually indicated for partial (grade II) ligament tears and occasionally for initial treatment in special circumstances. The ultimate goal of treatment is to return the patient to pre-injury employment or activity with the hope of delaying post-traumatic arthritis. The purpose of this manuscript is to 1) classify for the purposes of treatment for the spectrum of ligament tears included in the term “multiligamentous knee injury (MLKI),” 2) identify the reported incidence of these relatively infrequent injuries, and 3) propose a surgical treatment algorithm based upon the review of case series literature and clinical experience to assist decision-making when faced with this difficult problem.
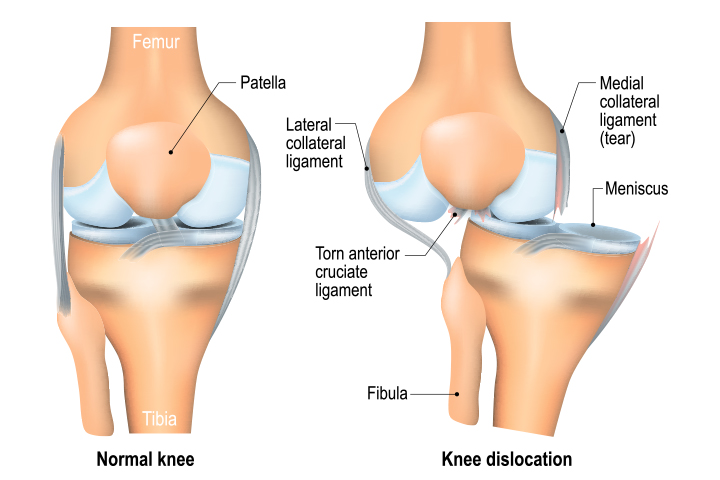
Knee Joint Anatomy
The knee joint is one of the largest and complex joints in your body. The joint is connected to your thigh bones and bones of the lower leg by various ligaments. The bones which meet to form your knee joint are the kneecap (patella), the thigh bone (femur) and shinbone (tibia).
The ligaments of the knee joint are:
- Anterior Cruciate Ligaments (ACL)
- Posterior Cruciate Ligaments (PCL)
- Medial Collateral Ligaments (MCL)
- Lateral Collateral Ligaments (LCL)
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT
“KNEEO Technique” For Knee Replacements
Symptoms of Multiligament Knee Injuries
The symptoms vary with the severity of the injury. They include:
- A loud popping sound occurring during injury
- Knee swelling
- A feeling of looseness in the knee joint
- Knee pain that may be sudden and severe
- Pain with weight bearing on the injured knee
Types of Multiligament Knee Injuries
Multiligament knee injuries may be mild or severe. Mild sprains do not damage the stability of the joint. A tear in the ligaments may be partial or complete. Partial tears cause loosening of the joint whereas, complete tearing of the ligament causes the joint to be unstable.
Diagnosis of Multiligament Knee Injuries
Your doctor physically examines the knee joint and its mobility. Your doctor may order anX-ray to rule out a fracture and an MRI to identify the injured ligaments.
What Happens if Multiligament Knee Injuries are Left Untreated?
Multiligament knee injuries need immediate treatment as they may result in disruption of blood supply to the knee. Some nerves may be damaged and if left untreated, severe cases may even require amputation.
Treatment of Multiligament Knee Injuries
Your doctor will suggest various non-surgical methods to treat multiligament knee injuries. Surgery is an option if you do not respond to conservative treatment measures.
Non-Surgical Treatment
- You may respond to non-surgical treatment and recover from the injury if the damage occurs to the collateral ligaments on the outside and inside of your knee.
- Icepacks may be used every 3-4 hours to reduce pain and swelling.
- Stabilize your knee joint with a compression bandage and wearing a brace.
- Your doctors may prescribe medications to reduce pain and swelling.
- Strengthening exercises are necessary to stabilize your joint. Your physiotherapist will plan the types of exercise based on the severity of your injury.


