- Home
- Subacromial Bursitis
Subacromial Bursitis
Shoulder Subacromial Bursitis
Subacromial bursitis is a common cause of shoulder pain that is usually related to shoulder impingement of your bursa between your rotator cuff tendons and bone (acromion). Your subdeltoidbursae is a less commonly inflamed shoulder bursae Pain and tenderness around the shoulder, especially when raising the arm above the head, may be a sign of shoulder bursitis. Shoulder bursitis occurs when the large bursa near the top of the shoulder becomes inflamed. A diagnosis of shoulder bursitis is often accompanied by a diagnosis of shoulder impingement syndrome or other shoulder problems. The shoulder’s soft tissue structures (muscles, ligaments, tendons, and bursae) are packed closely together, so their health is interdependent. If one becomes damaged, others are likely to become damaged, too.
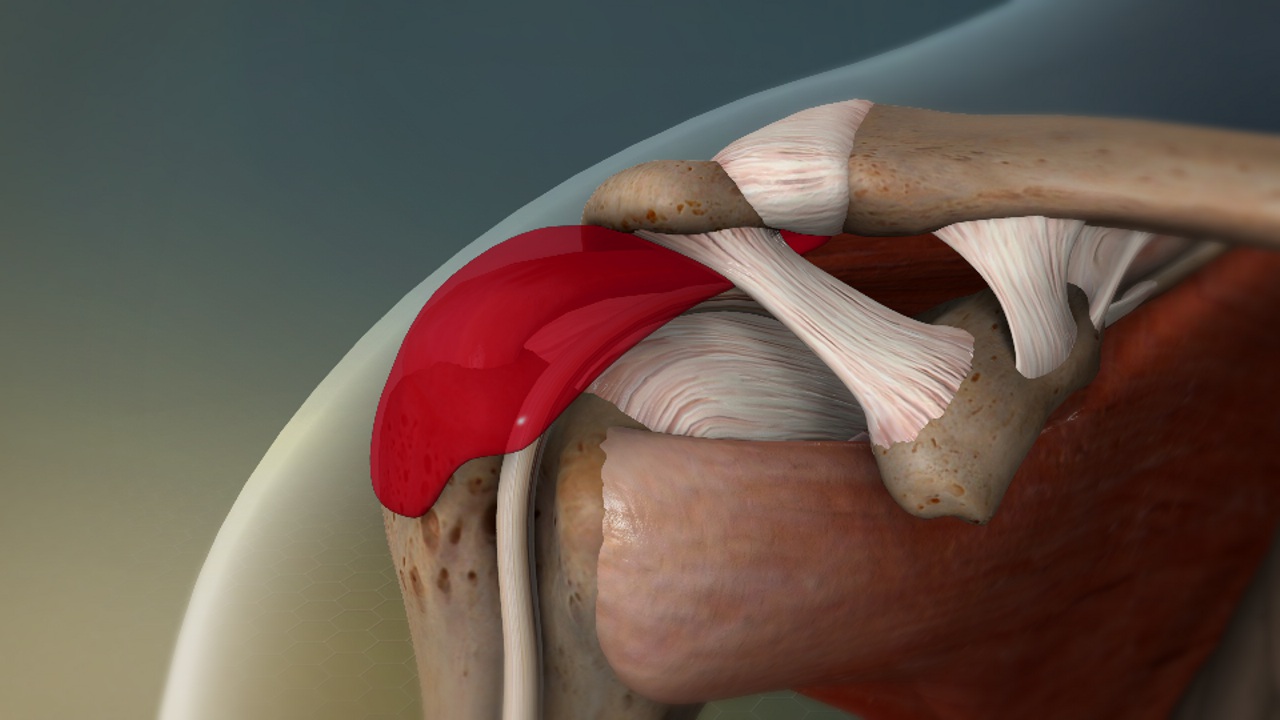
Small changes to the bursa can lead to bursitis symptoms
Subacromial bursitis is a common cause of shoulder pain that is usually related to shoulder impingement of your bursa between your rotator cuff tendons and bone (acromion). Your subdeltoidbursae is a less commonly inflamed shoulder bursae Pain and tenderness around the shoulder, especially when raising the arm above the head, may be a sign of shoulder bursitis. Shoulder bursitis occurs when the large bursa near the top of the shoulder becomes inflamed. A diagnosis of shoulder bursitis is often accompanied by a diagnosis of shoulder impingement syndrome or other shoulder problems. The shoulder’s soft tissue structures (muscles, ligaments, tendons, and bursae) are packed closely together, so their health is interdependent. If one becomes damaged, others are likely to become damaged, too.
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT
“KNEEO Technique” For Knee Replacements
The Subacromial Bursa and Bursitis
The purpose of a bursa is to provide a cushion and reduce friction between hard bone tissue and adjacent soft tissue. There are more than 140 bursae in the body,1 and the shoulder’s subacromial bursa is one of the largest.2
All bursae are a thin, slippery, fluid-filled sacs. Each is composed of:
- A thin outer membrane, called the synovial membrane or synovium
- An inner fluid, called synovial fluid
The subacromial bursa is located below a part of the shoulder blade called the acromion (hence the name “subacromial”).
- The acromion is the topmost part of the shoulder blade. It forms the bony top of the outer shoulder.
- The acromion lies above the bones that form the shoulder’s ball-and-socket joint (glenohumeral joint).
- In most people, there is 1 cm to 1.5 cm of space between the acromion and the shoulder’s ball and socket. This small space is called the subacromial space.
- Sandwiched in the subacromial space are rotator cuff muscles, tendons, and the subacromial bursa.
- The subacromial bursa provides a cushion and reduces friction between the shoulder’s muscles and tendons and the acromion.
When the arm is raised up, particularly up and out to the side, the subacromial space becomes smaller, and soft tissues may be pinched.
Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
Shoulder impingement syndrome is an umbrella term that describes the painful pinching of soft tissue when the arm is raised, and it is considered the most common cause of shoulder pain.
- Shoulder bursitis, in which the bursa is inflamed and swollen,
- Tendonitis, in which a tendon is inflamed and swollen (the biceps tendon, which connects the biceps muscle to the shoulder socket, is commonly affected).
- Acromioclavicular arthritis, a rotator cuff tear, or another shoulder condition that causes the subacromial space to shrink; this shrinking leads to irritation of the bursa and tendons, eventually resulting in bursitis or tendonitis


