- Home
- Sudecks Osteodystrophy/ Shoulder Hand Syndrome/ CRPS
Sudecks Osteodystrophy/ Shoulder Hand Syndrome/ CRPS
Sudecks osteodystrophy
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), also known as reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD), is a disorder of a portion of the body, usually the arms or legs, which manifests as pain, swelling, limited range of motion, and changes to the skin and bones. It may initially affect one limb and then spread throughout the body; 35% of affected people report symptoms throughout their whole bodies.There are multiple names for this disease, as well as two subtypes.
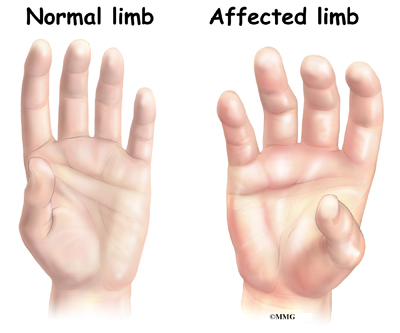
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
The symptoms are variable and will present themselves differently from patient to patient. The main symptoms are –
- a generalised burning pain
- changes in the skin, which may become shiny
- swelling
- more perspiration more than usual
- muscle wastage
- stiffness in the affected part
- increased sweating
likely to have one of the three following types of disease progression:
- “Stage” one is characterized by severe, burning pain at the site of the injury, muscle spasms, joint stiffness, restricted mobility, rapid hair and nail growth, and vasospasm.
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT
You Don't Have To Live With Pain
Dr. Rahul Bade is a specialist Knee & Shoulder Surgeon.
- The vasospasm is that which causes the changes in the color and temperature of the skin. Some may experience hyperhydrosis (increased sweating). In mild cases this stage lasts a few weeks, in which it can subside spontaneously or respond rapidly to treatment (physical therapy, pain specialist).
- “Stage” two is characterized by more intense pain. Swelling spreads, hair growth diminishes, nails become cracked, brittle, grooved and spotty, osteoporosis becomes severe and diffuse, joints thicken, and muscles atrophy.
- “Stage” three is characterized by irreversible changes in the skin and bones, while the pain becomes unyielding and may involve the entire limb. There is marked muscle atrophy, severely limited mobility of the affected area, and flexor tendon contractions (contractions of the muscles and tendons that flex the joints). Occasionally the limb is displaced from its normal position, and marked bone softening and thinning is more dispersed.
TREATMENT
The goal of treatment is the preservation of the normal functionality of the affected body part, that is to say, the mobility of the extremities. Treatment requires patience from the patient and physician. It is very difficult to influence the course of the disease and the psychological burden caused by the pain is very important.
Medical treatment:
Tentative evidence supports the use of bisphosphonates, calcitonin, and ketamine. Doing nerve blocks with guanethidine appears to be harmful. Evidence for sympathetic nerve blocks generally is insufficient to support their use. Intramuscular botulinum injections may benefit people with symptoms localized to one extremity.
- Ketamine
Ketamine, a dissociative anesthetic, appears promising as a treatment for complex regional pain syndrome. It may be used in low doses if other treatments have not worked. No benefit on either function or depression, however, has been seen. - Bisphosphonate treatment
Very limited data reviewed showed that bisphosphonates have the potential to reduce pain associated with bone loss in patients with CRPS I.
Surgery
It is required when medication and conservative treatment are failed and mostly used in sever CRPS. Following are the procedures:
- Spinal cord stimulators
- Sympathectomy
- Amputation
Physiotherapy Treatment
It is important that the patient actively participates and takes its responsibilities during treatment.
- First of all, to rest; possibly splinting
- Elevation of the affected
- Cool slightly (NOT ice), carbon dioxide baths costs
- Manual lymphatic drainage
- Electrotherapy, IFT, TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation: inhibition of conduction of pain due to nerve stimulation by electrical current)
- Massages of connective tissue
- Mobilization in chronic phase
- Carefully active movement of affected limb
- Occupational therapy to maintain mobility
- Specific training with specialists
- Learning relaxation techniques
- Aquatic therapy allows activities to be performed with decreased weight bearing on the lower extremities
- Mirror therapy
- Gradual weight bearing
- Regular Gradual Stretching exercise in Pain free mode


